Query Builder
Jetstream's query functionality provides an easy and powerful way to view your record data and even metadata records, like Validation Rules.
Not only is the query builder great for viewing record data, but is also a great place to view your objects and fields along with a ton of useful information like field API names, picklist values, field dependencies and more.
Basic query
- Select the object that you would like to work with
- Choose the fields that you would like to include in your query
- Optionally add
- Filters that will limit the records
- ORder by to change the order of the records
- Limit to limit the number of records
- Click execute
You have run your first query! 🎉
Jetstream is designed to be fast and easy to run queries without having to schedule tasks and wait for things to finish. Click to Go Back to run another query.
Query configuration
Fields
Selecting related fields
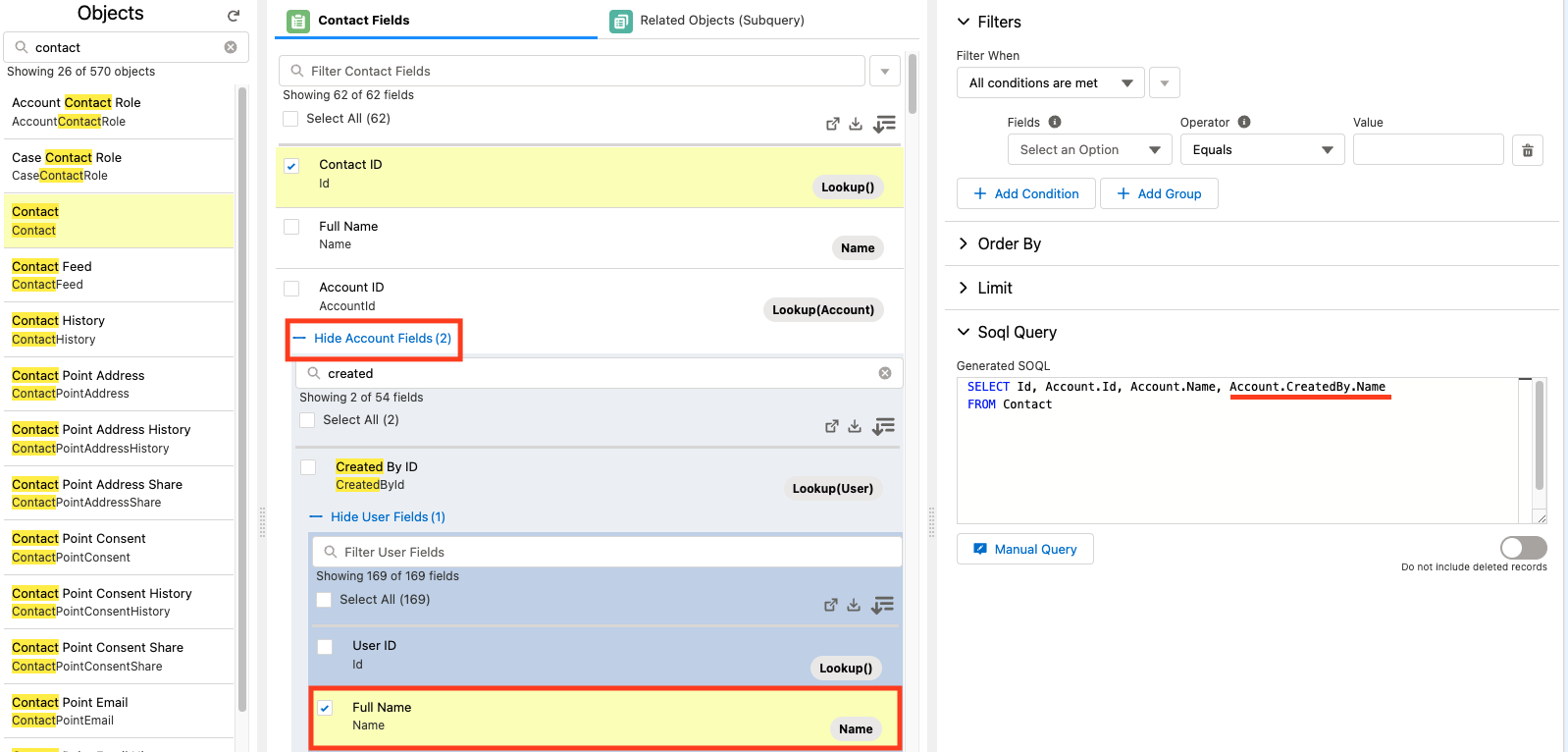
Jetstream allows you to include related records through up to 6 relationships.
To include related fields, find a related field, such as the Account lookup on a Contact, and click View Account Fields.
Once expanded, you will see the button changes from View to Hide and as you select fields, the number of selected fields will show so you can easily see which fields are selected even if the lookup is collapsed.
Field filters
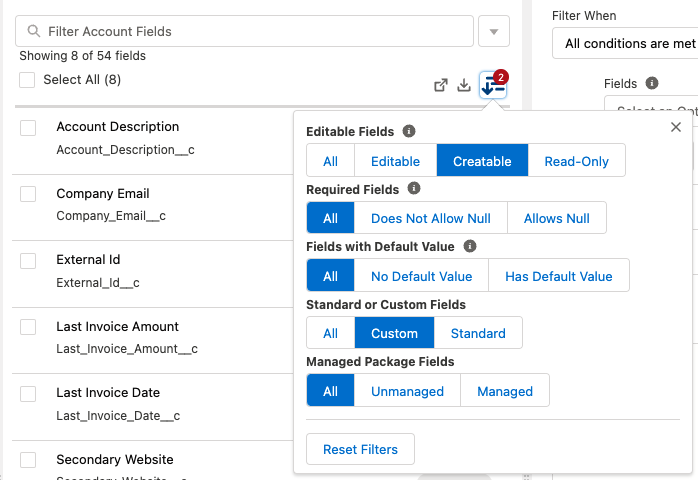
Click the filter icon to open up the quick filter.
From here, you can quickly change which fields are visible to select using one of the following options:
- All Fields
- Creatable Fields
- Updateable Fields
- Custom Fields
- Non-Managed Fields
- Non-Managed Custom Fields
- Selected Fields
When you have an active filter applied, you will notice the icon changes color and the number of active filters is shown.
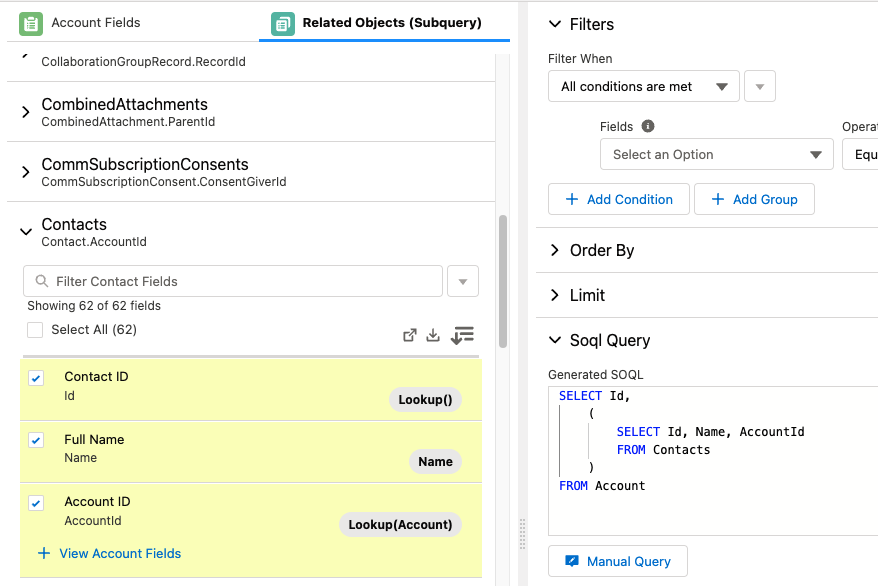
Selecting children objects (Related Lists)
Click the Related Objects (Subquery) tab to show all the child objects. Any object that has a lookup field to the current object will show up in this list, just like Related Lists show up in Salesforce.
Standard Options
Filters
Filters allow you to limit which records are returned from Salesforce.
- Filter When all conditions are met requires all conditions to be true AND
- Filter When any conditions are met requires at least one condition to be true OR
- You can use groups to mix and match AND and OR conditions.
Choose the field, operator, and value to complete the filter.
Depending on which field you select, the value may change to give additional configuration options. For example, if you choose a Date you use a date picker
- Use contains, starts with, or ends with to perform partial matches.
- If you want to find records from a specific date range, use Relative Values to keep things simple, or use greater than or less than with the date picker.
- If you want to filter against a list of values, such as a list of Ids or Product Codes, use the IN or NOT IN operator.
- To see if specific values in a multi-select picklist are selected, use the Includes or Excludes filters.
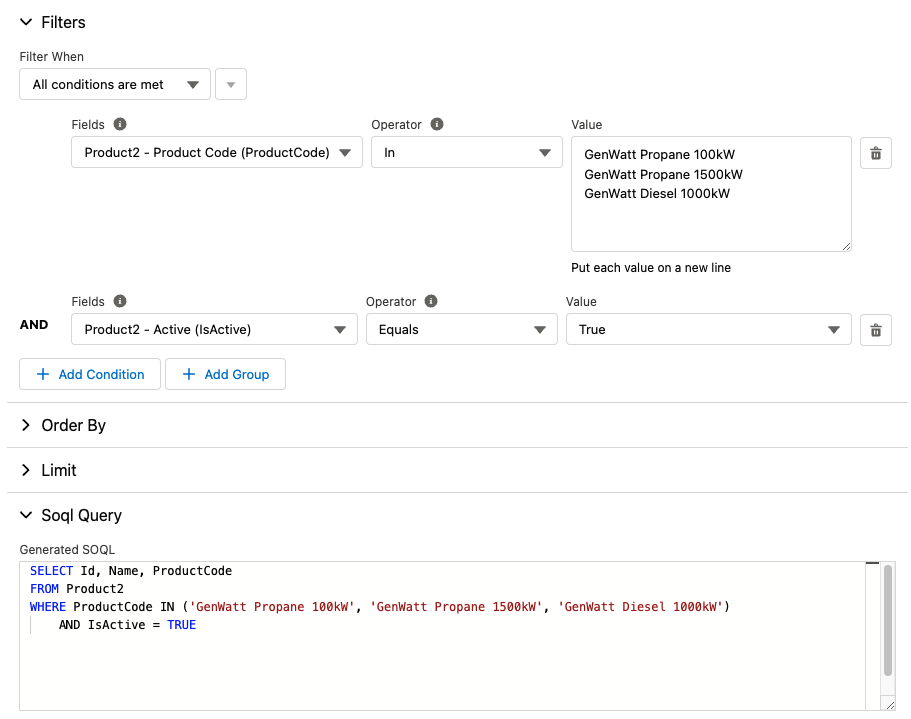
Example
Here is an example that will find all the products that have a product code matching one of three products codes that are also active.
If you have a list of values, like Ids or picklist values, utilize the IN operator.
If you want to look up just one record by Id, use the View Record Details button at the top of the page (or press cmd+k or ctrl+k) to view full record details by id.
Order By
Order by allows you to sort the returned records. In addition to choosing the sort order, you can also choose if records with blank values are sorted with higher or lower precedence compared to records with values.
You can add multiple Order By clauses.
Limit and Skip
Limit allows you to choose the maximum number of records that can be returned from a query.
Skip allows you to skip some number of records in the return set. This is normally paired with Limit.
Advanced Options
The advanced options allows configured complex SOQL queries using field functions and GROUP BY clauses. Refer to the Salesforce documentation to understand how these work and understand under what circumstances various functions and group by clauses are available for use.
On the right hand section of the page, choose the "Advanced Options" tab to access these features.
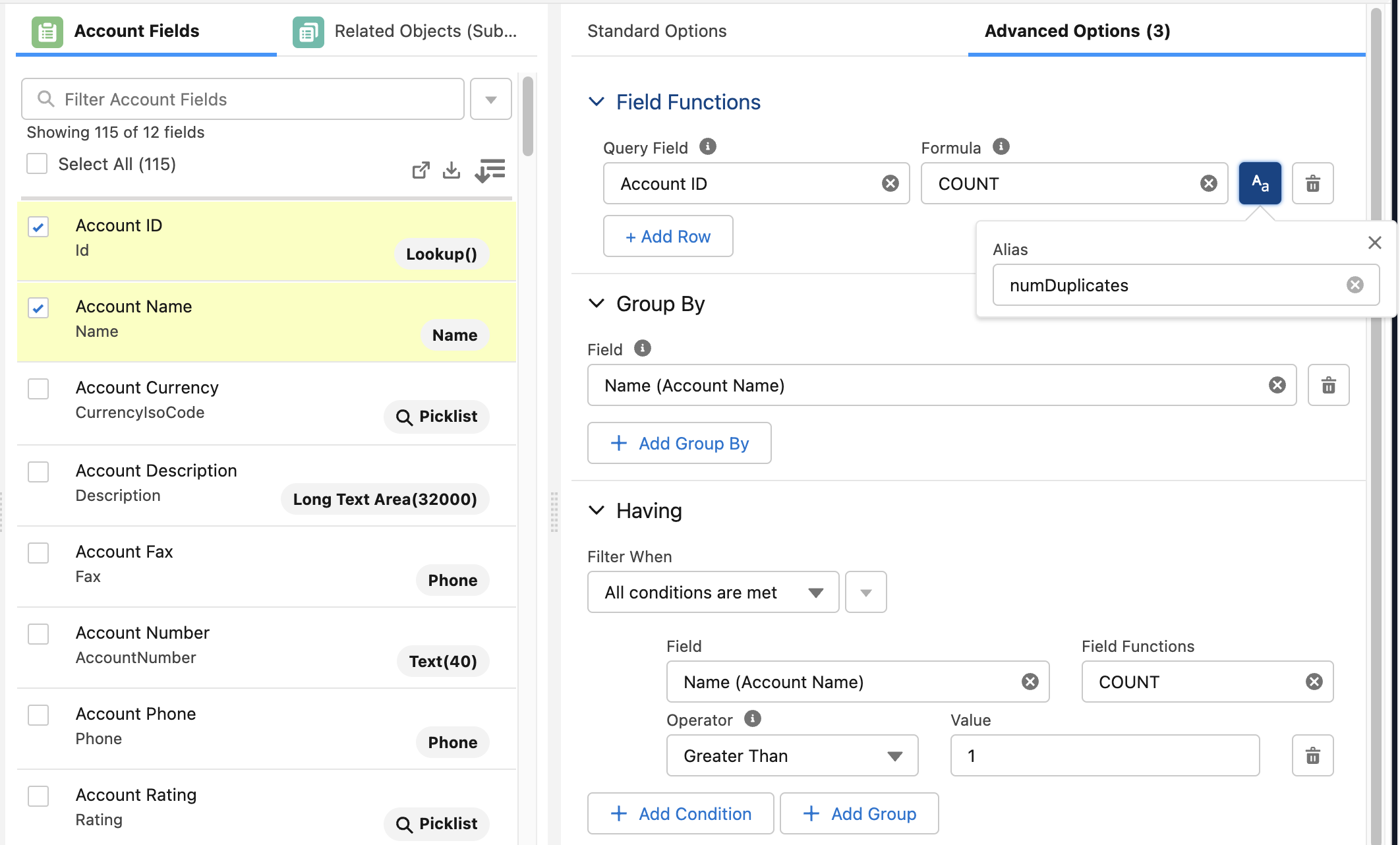
Here is an example of a Group By SOQL query that can be generated with Jetstream. This query will identify the number of Accounts that have duplicate names.
NameWas added as a Group By and also selected to know what the name of the duplicate is.- The
COUNTfunction was applied toIdto count the number of records grouped and the field was given an alias ofnumDuplicates(otherwise the column would be auto-named asexpr0). - There is a Having clause to only return accounts where there are at least two records that will be grouped.
SELECT COUNT(Id) numDuplicates, Name
FROM Account
GROUP BY Name
HAVING COUNT(Name) > 1
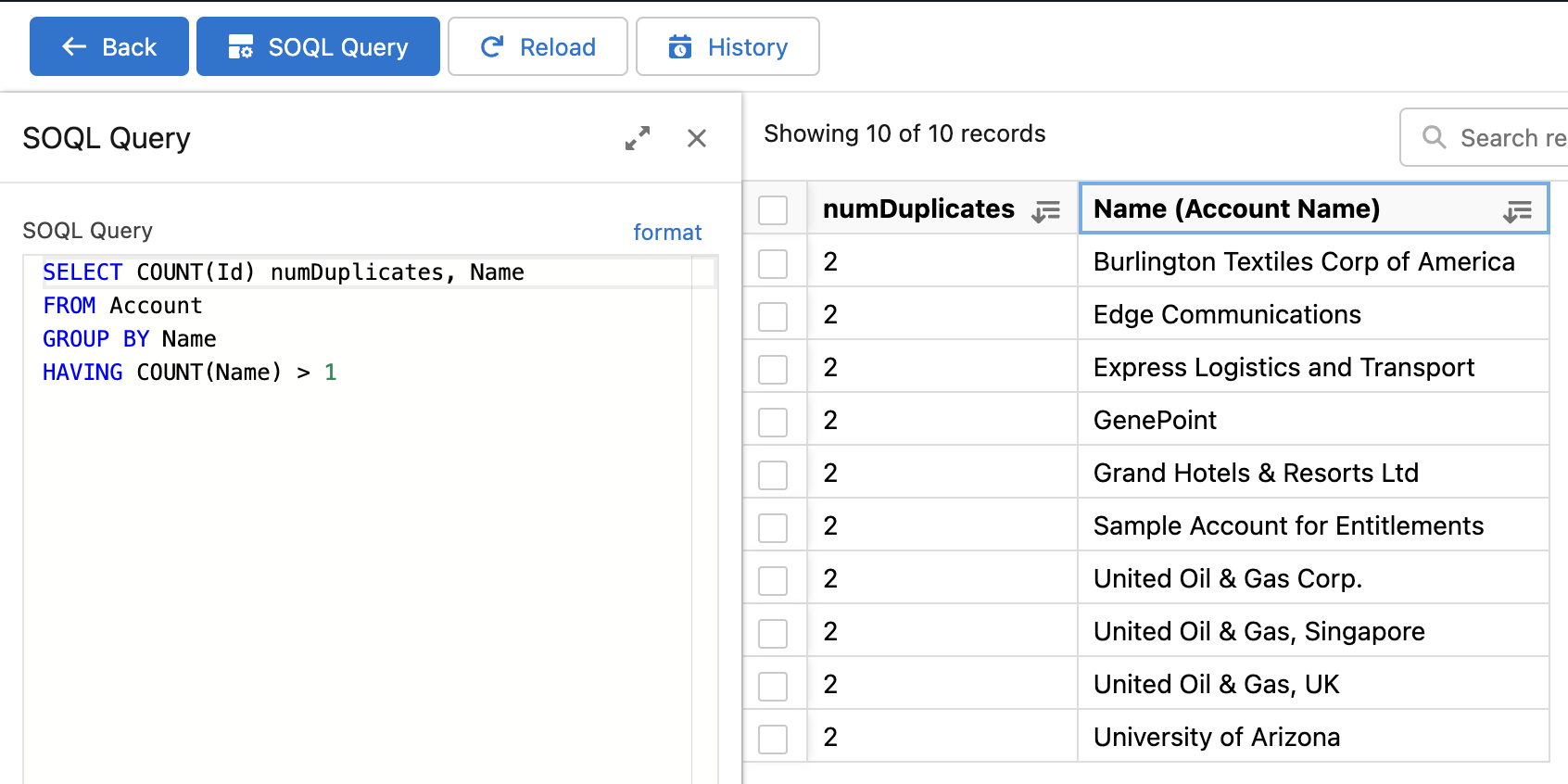
Here are the results:
Field Functions
Field functions change the value returned for a field.
Only fields you have selected in your Query will be available for selection because these functions can only modify fields included in the query.
Depending on the type of field you have selected and if you have included a Group By clause will determine what type of functions are available for each field.
FORMAT and COUNT are available for all fields.
Picklist fields have the toFormat formula available that will show the translated version of a field.
Currency fields have the ConvertCurrency function available but can only be used if your org has multi-currency enabled.
If you have a GROUP BY clause configured, then all date and datetime fields have a variety of functions that can be used.
Group By
Group By allows summarizing records and combines groups of records into an individual query result.
You can add multiple group by fields to your query as dimensions to group your records. Any fields included in your query must either be in your group by clause or must have an aggregate function applied (e.x. COUNT of SUM)
Review the Salesforce documentation for more information.
Having
Having is just like normal query filters, but must be combined with a group by clause and will be applied after the grouping has taken place. You can include aggregate functions in your having clause, which are not available in normal query filters.
Query history
Jetstream will save your recent queries so you can easily execute them again in the future. Click the Query History button to view your history.
You can save queries that you want to be able to find easily in the future, click the Plus icon to save the query.
From query history you can choose either Restore or Execute.
Restore will configure the query page with all the checkboxes and filters configured just like the first time you executed the query so that you can easily start where you left off and make changes. If there are any parts of the query that could not be restored, you will be notified.
Executing the query will run it and show the results.
Query history is stored locally in your browser, so if you change browsers or computers, your query history will not follow you.
Manual query
If you have a SOQL query and you want to use that on the Query builder, then you click the Manual Query button at the top of the page and paste in your query and restore or execute.
Clicking restore will reset the page to match the provided query. This is really useful if you have obtained a query from somewhere else and want to make changes to it using the query builder.
Querying metadata records
In addition to regular metadata, you can also query metadata records. Click the change object icon to switch between object and metadata query.
After changing to a metadata object, everything else about the query builder is identical to regular record queries.
Your query history will be saved for Metadata queries and will have a different icon to make it easy to see which items in your history are regular records or metadata.
When querying metadata records, if you include the FullName or Metadata fields, Salesforce only allows one record to be returned. It is better to leave these off initially unless you want to see the detailed information for just one record.